
The way to configure conditional breakpoints may be different in different IDE versions.
INTELLIJ IDEA DEBUG CODE
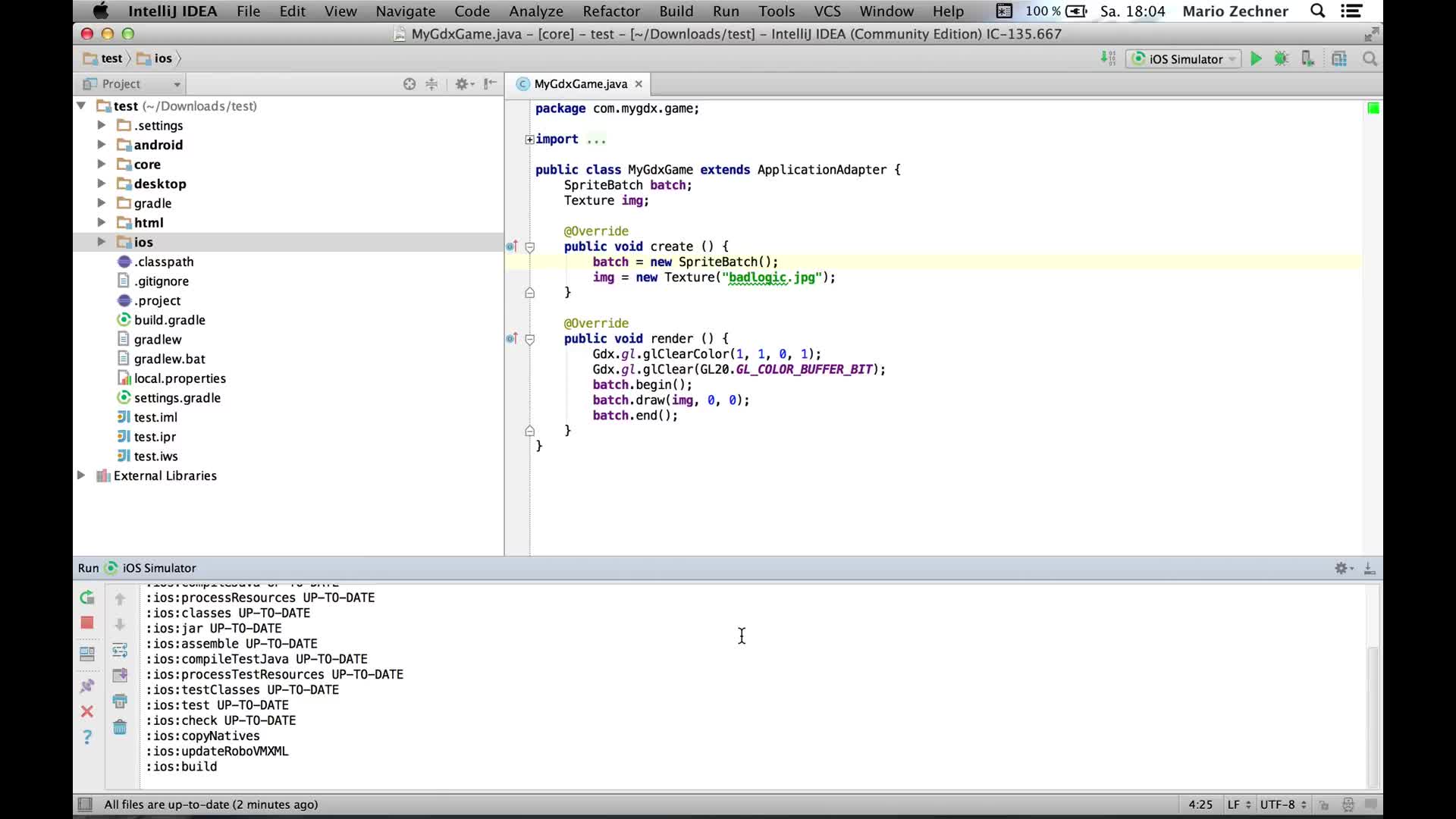
The Editor Running Code Running Tests Debug Mode. You can confirm that 'Thread 1' was executed and didn't get suspended through the following steps:ġ.In the console, you can verify through the logs that 'Thread 1' ran and exited.Ģ.In the Threads pane, you can check that there is no 'Thread 1' On writing code, debugging code, and running tests in IntelliJ. When the app pauses, only 'Thread 2' is suspended. This condition ensures that the debugger would pause the current thread only if that thread's name is 'Thread 2': Then we add the condition as shown in the screenshot below. After adding a breakpoint, right-click on it, check 'Suspend' and select 'Thread'. We can use conditional breakpoint feature. On the Server tab, set On frame deactivation to Do nothing.
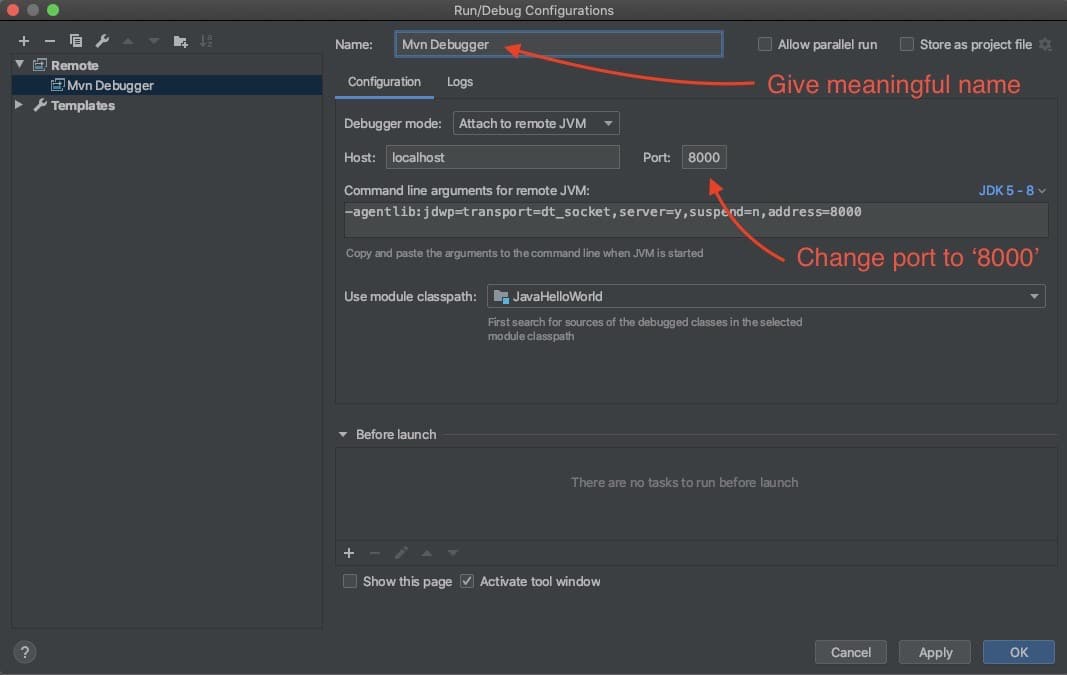
Open the Run/Debug Configurations for the corresponding application server via Run > Edit Configurations. This includes 'Thread 1' and 'Thread 2' for our app. IntelliJ IDEA ¶ The JRebel plugin for IntelliJ IDEA includes the JRebel agent and helps you to automatically generate the JRebel configuration. But we will run into a problem - all the threads that encounter the breakpoint will be suspended. This suggests that I need to add a breakpoint on the first line of FactorialCalculatingThread's run() method (line 39). You can double click on each thread to observe their call stacks.Īssume that I am troubleshooting a bug in this program and I need to pause execution only for 'Thread 2' as soon as it starts running. When the app pauses at that breakpoint, we should see at least three threads - 'main', 'Thread 1' and 'Thread 2' in this pane (check screenshot below). Referring to the code above, I have added a breakpoint at thread1.join()(on line 18). Thread pane shows all the threads that are currently active. If you want to check call stack of other threads, you can select them from the drop down. In the image below, the breakpoint is in the main() method and the Frame is showing us the call stack for the main thread. It focuses on the thread which is currently paused because of the breakpoint and shows the call stack of that thread. When the code reaches the line where there is a breakpoint, IntelliJ IDEA will stop the server from running more code, and now you can step through the code and. Go to a DOS prompt and kick off your client code that calls this method. The Debug tool window has Frame pane which consists of a drop down. Now IntelliJ IDEA is ready to debug the serverside code, when that code actually gets called on the App Server. 2019.2.2 (CE)) tools that I often use while debugging a multithreaded app. Similarly, we call thread2.join() Use of Thread.join() method ensures that sum (on line 25) is not calculated until both the threads return, that is, addition is performed only after we get the factorials of 100. Then in the main() method, we call thread1.join() so that the main thread won't execute further until 'Thread 1' returns. Here is what is happening in the above code: We initialize, name, and start two threads - 'Thread 1' (to calculate 100!) and 'Thread 2' (to calculate 100000!).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
